Daltons law is an ideal gas law. A solution is considered ideal when the interactions between.

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Dalton S Law 11th Chemistry Chemistry
Although the problem does not explicitly state the pressure it does tell you the balloon is at standard.

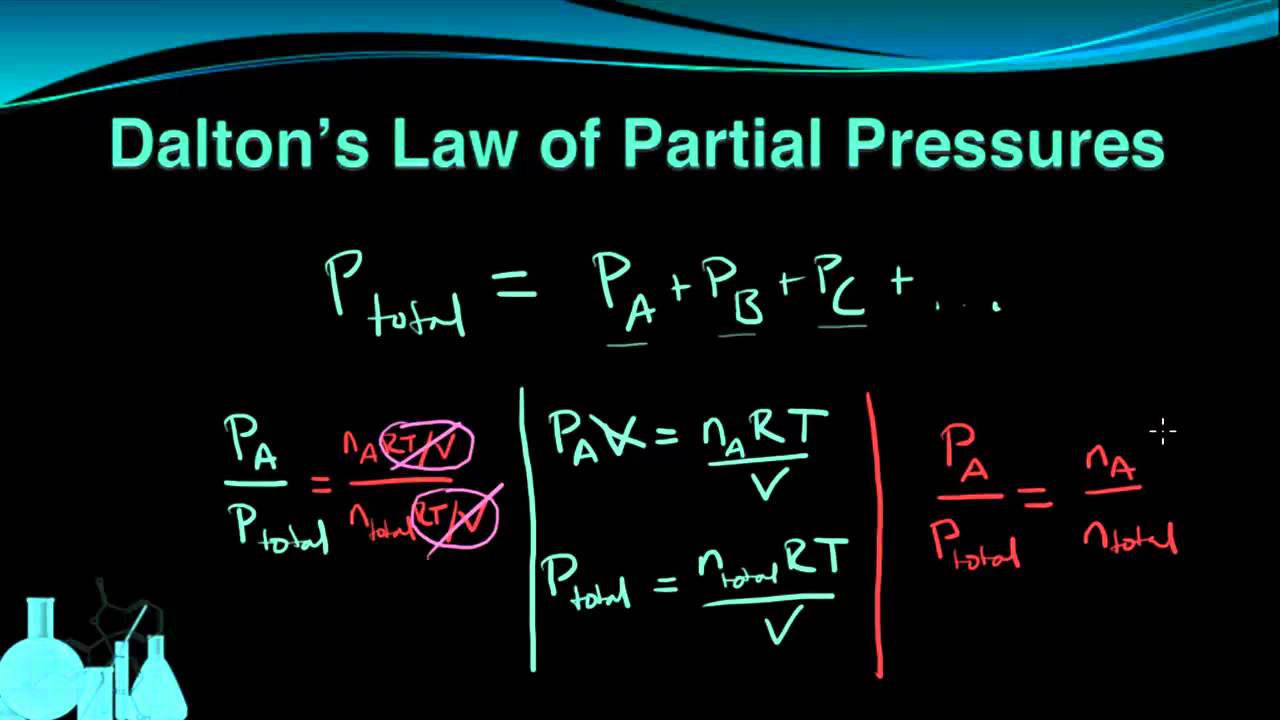
. Understand Daltons Law of Partial Pressures. Daltons Law of partial pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. The partial pressure is the pressure that each gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture at the same temperature.
Raoults law states that. Developed by chemist and physicist John Dalton who first advanced the concept of chemical elements being made up of atoms 9 X Research source Daltons Law states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the pressures of each of the gases in the mixture. Since equal volumes have equal number of molecules this is the same as being inversely proportional to the root of the molecular weight.
At high pressure the volume occupied by a gas becomes significant when compared to the free space between particles. To Learn expressions on Daltons law of partial pressure Examples Videos with FAQs. Daltons Law of partial pressure for moist air can be expressed as.
P i the. The total pressure of the gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressure of the component gases. P x P Total n x n Total where P x partial pressure of gas x P Total total pressure of all gases n x number of moles of gas x n Total number of moles of all gases Step 1.
This new pressure is the partial pressure of each A and B and is given by Raoults law and depends on the concentration of each component in the liquid phase. The vapor pressure of a solution is equal to the vapor pressure of a pure solvent times its mole fraction. Raoults law is only accurate for ideal solutions.
Definition of partial pressure and using Daltons law of partial pressures If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Therefore the directions of diffusion during gas exchange in the lungs and in body tissues are based on the differences in partial pressure of. The limitations of Raoults Law are as follows.
The total pressure of air or standard atmospheric pressure is 29921 inches of mercury so the partial pressure of the dry. Sum of all partial pressure is the total pressure of that gas mixture a physical law called the. P tot the total pressure.
The deviation from the law increases with increasing pressure. Its also expressed by the following equation. P p a p w 1 where.
A mixture of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas exerts a total pressure of 15 atm on the walls of its container. Visit BYJUS for more content. P total pressure of air Pa Nm 2 p a partial pressure dry air Pa Nm 2 p w partial pressure water vapor Pa Nm 2.
Daltons law the statement that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual component gases. It is only an approximation for real gases. P tot P i P 1 P 2 P 3.
PA XA PB XB XAPA XBPB. Where P is the mole fractions of the components. Partial pressure blending is commonly used for breathing gases for diving.
Volumetric gas fraction converts trivially to partial pressure ratio following Daltons law of partial pressures. Daltons law of partial pressures must be applied. The gases present in the container are chemically inert.
Partial pressure blending at constant temperature is computationally simple. The partial pressure is the pressure each gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture. The accuracy required for this application can be achieved by using a.
If the partial pressure of hydrogen is 1 atm find the mole fraction of oxygen in the mixture. The term partial pressure is used when we have a mixture of two or several gases in the same volume and it expresses the pressure that is caused by each of the induvidual gases in the mixture. Solved Examples on Daltons Law of Partial Pressure Example 1.
This empirical relation was stated by the English chemist John Dalton in 1801. Daltons Law primarily applies to ideal gases rather than real gases due to the elasticity and. Daltons law is as.
Limitations of Raoults Law. Given P hydrogen 1 atm P total 15 atm. Combined with Avogadros law ie.
Partial Pressure- Partial Pressure is defined as a container filled with more than one gas each gas exerts pressure. The pressure of any gas within the container is called its partial pressure. In 1803 this scientific principle officially came to be known as Daltons Law of Partial Pressures.
Deviations From Daltons Law. Partial pressure is found by Daltons Law. Daltons law of partial pressures states that the pressure of a mixture of gases simply is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual components.

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Explained Dalton S Law Medical Anatomy Respiratory Therapy
Chemistry 7 6 Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Dalton S Law Chemistry Dalton

15 12 6 Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure In Mixtures Of Gases Each Component Gas Behaves Independently Of The Other S In 2022 Ideal Gas Law Molecular Physics Formulas

Daltons Law Of Partial Pressures Easy Science Dalton S Law Easy Science Organic Chemistry Study
0 Comments